Sustainability reporting software for mining and minerals
The world’s only sustainability analytics solution designed for minerals and mining
With MS Sustainability you can track indicators such as GHG emissions (Scopes 1, 2 & 3), water, energy, air quality, waste, hazardous materials, pollutants and other climate and nature-related risk factors with proven assurance.
A new era of accountability is here
For the energy-intensive mining and minerals sector, legislators and market sentiment have aligned to demand sustainability reporting transparency and climate and nature risk disclosure.
As new compliance standards roll out globally, sustainability reporting has moved from a voluntary nice-to-have to a mission-critical mandatory activity with significant real-world consequences for failing to comply.
Key reporting frameworks in place include the ISSB (Industrial Sustainability Standards Board), CSRD (EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) and SEC (US Securities and Exchange Commission).
Disclosure requirements are more granular. Many sustainability frameworks require auditable reports down to a product level, scenario analysis to demonstrate climate resilience, double materiality reporting, and disclosures on carbon, water, waste, energy and other sustainability indicators.
Innovative resources companies are embracing intelligent digital tools to meet this challenge.
Stay across the latest reporting requirements:
What to look for in digital sustainability reporting software
When choosing digital sustainability reporting software, you’ll need a solution that delivers granular data, offers compliance with evolving frameworks, and enables you to set and meet decarbonisation targets.
Data: Capture | validate| contextualise | manage | report
Complex industrial processes like mining require a specialised approach to sustainability reporting that starts with advanced data capture and processing. The need for granular activity data requires a mass and energy balance to track every step of the production process across the value chain.
Data capture
- Automated data capture across the industrial facility, both quantitative and qualitative.
- Source data from instrumentation (IoT), laboratory information management systems (LIMS), data historians, ERP systems, environmental systems and manual data entry.
Data validation
- Organises, cleans and validates data.
- Automated alerts and monitoring.
- Data health checks.
Data contextualisation
- Digitally simulate the industrial process and calculate a second comparable set of data to contextualise data and complete data gaps.
- Conduct a mass and energy balance of your industrial facility to identify process optimisation opportunities and to calculate and validate the most accurate and auditable finance-grade activity data.
Data management
- Securely store data in a multi-dimensional database.
Data reporting
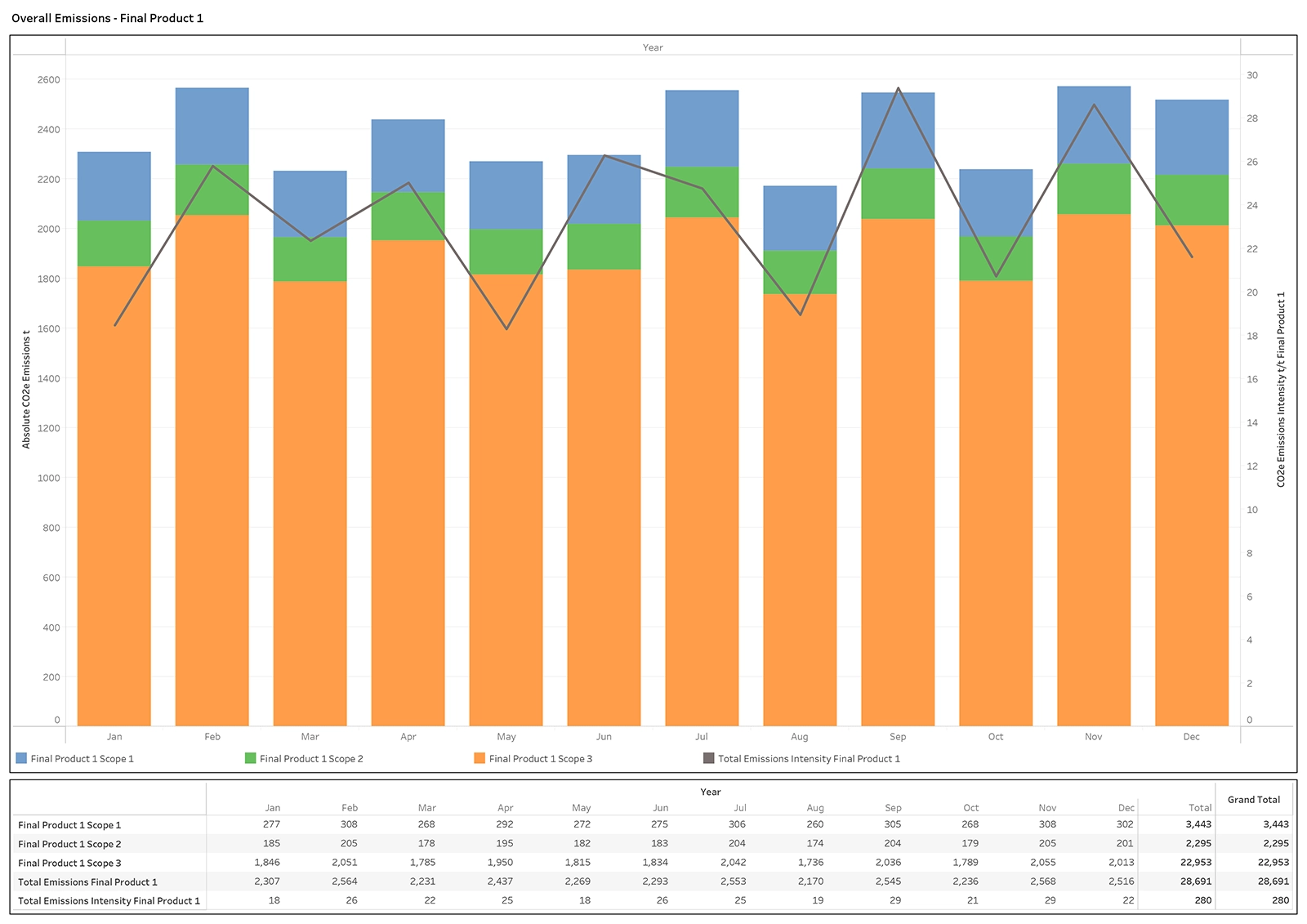
- Report by country, site, boundary (corporate, financial reporting hierarchy or site internal boundaries), scope 1, 2 & 3, scope categories and product level (product carbon footprinting PCF).
- Granular data that can be configured to report across any framework.
Data auditability
- Attach image files and documents to support audit requirements.
- User activity logs.
- Track data down to its source, e.g. instrumentation reading.
Digital taxonomy
- Data tagging to data points/measure points within framework disclosures into a machine-readable format according to multiple digital taxonomies.
Compliance: Satisfy evolving global frameworks
In this new era of legislated accountability, your sustainability reporting solution will need the features and flexibility to meet a host of new and evolving regulations, including:










Decarbonisation: Target & transition planning | Scenario analysis & climate resilience
Beyond ticking the compliance boxes, your digital solution must cater to frameworks that require target setting, monitoring and tracking, as well as scenario analysis to test business resilience to various physical and transition risks.
Target and transition planning
- Disclosure of sustainability and climate-related targets set by the company and the jurisdiction in which they operate and how these have been informed by the latest international agreement.
- Other analysis used in transition planning, such as varying inputs into scenario analysis to test and plan decarbonisation projects, such as marginal abatement cost curves.
Scenario analysis and climate resilience assessment
- Scenario analysis is to be used in some frameworks to assess a company’s climate resilience. Disclosure is required on whether and how the scenarios used align with international agreements on climate change.
Why MI Sustainability?
Available as a stand-alone solution or add-on to MI Core, MI Sustainability enables you to produce accurate data-driven sustainability reports to satisfy evolving global legislative frameworks and set and achieve decarbonisation targets.
Unique in the market, MI Sustainability is:
- Purpose-built for complex metals and minerals organisations to handle millions of data points.
- Enables granular and auditable reports across Scopes 1, 2 & 3 down to climate and nature-based indicators and calculates a product carbon footprint (PCF).
- Makes sustainability reporting and compliance easy with digital reports to meet any framework across any jurisdiction.
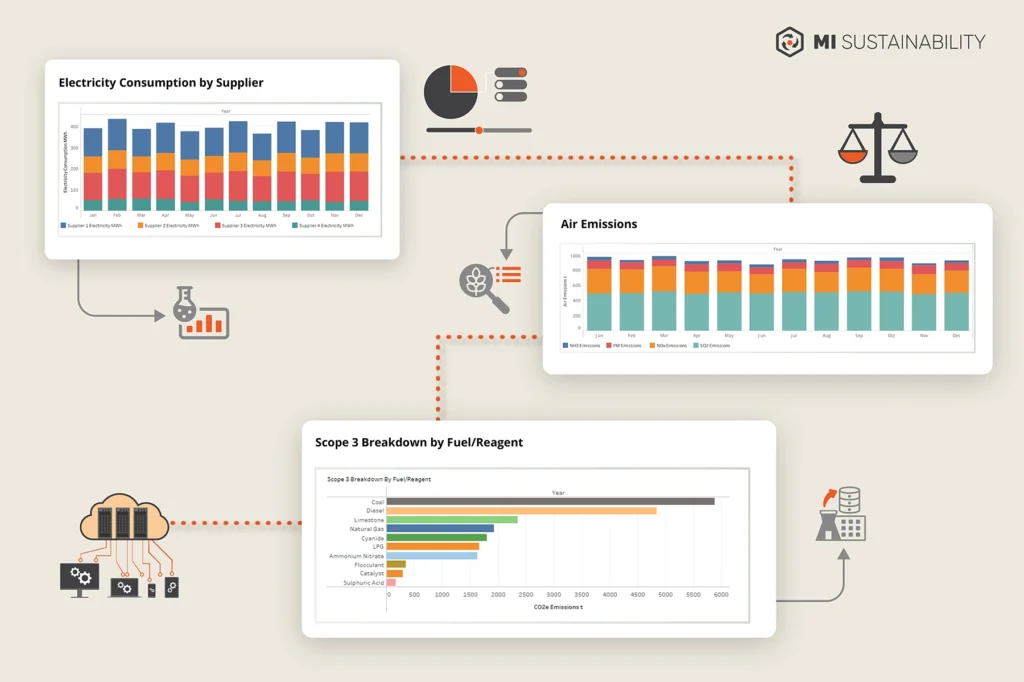
How MI Sustainability works
MI Sustainability integrates granular plant-wide data capture and analytics, is compatible with major global compliance frameworks and has advanced decarbonisation capabilities. Click on each layer to learn more.
Layer 1: ESG data centralisation, organisation & validation
Gathers transactional ESG data from disparate sources, including:
- Plant data / data historians
- Laboratory information systems (LIMS)
- Environmental systems
- Health and safety systems
- Human capital management data
- Mining / Manufacturing planning systems
- Manual data entry
- ERP solutions
- Supply chain data
Layer 2: ESG data contextualisation (simulated mass & energy balance)
Consolidates multiple data sets, including:
- Activity data
- GHG emissions data
- Environmental data â climate and nature
- Social data
- Governance data
- ESG digital taxonomy
Layer 3: Enterprise ESG control panel
The workflow and analytics layer where users manage functions such as:
- Disclosures approval workflow
- Materiality assessment tools
- ESG audit tools
- Data quality analysis
- Manual data entry
Layer 4: Reports, analysis & visualisation
The primary user interface layer to run and view reports, including:
- Regulated and voluntary ESG disclosures
- Sustainability reporting across frameworks
- ESG targets and transition planning
- Scenario analysis and resilience assessments
- Process optimisation
MI Sustainability features
One solution for granular, finance-grade auditable reports
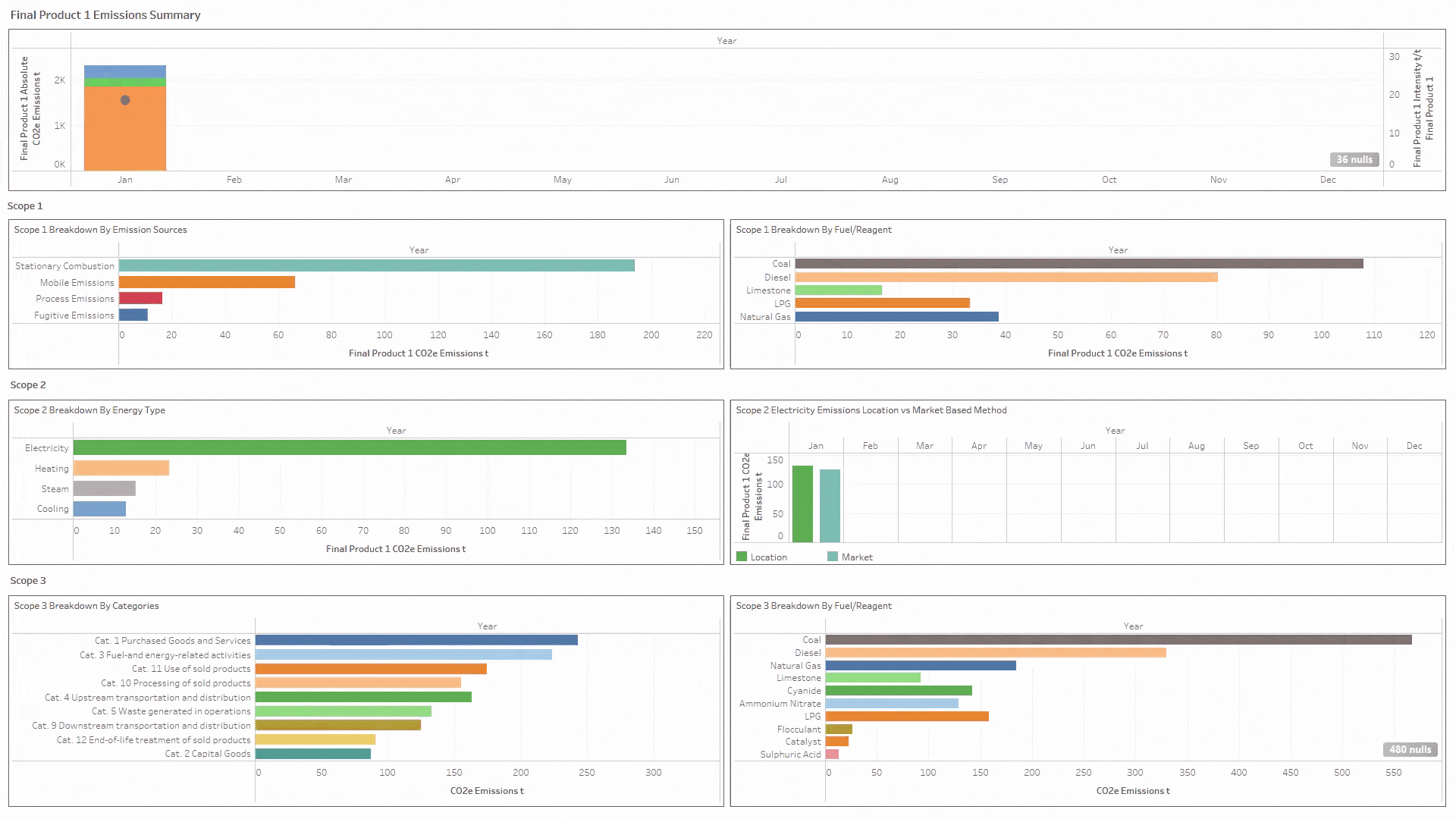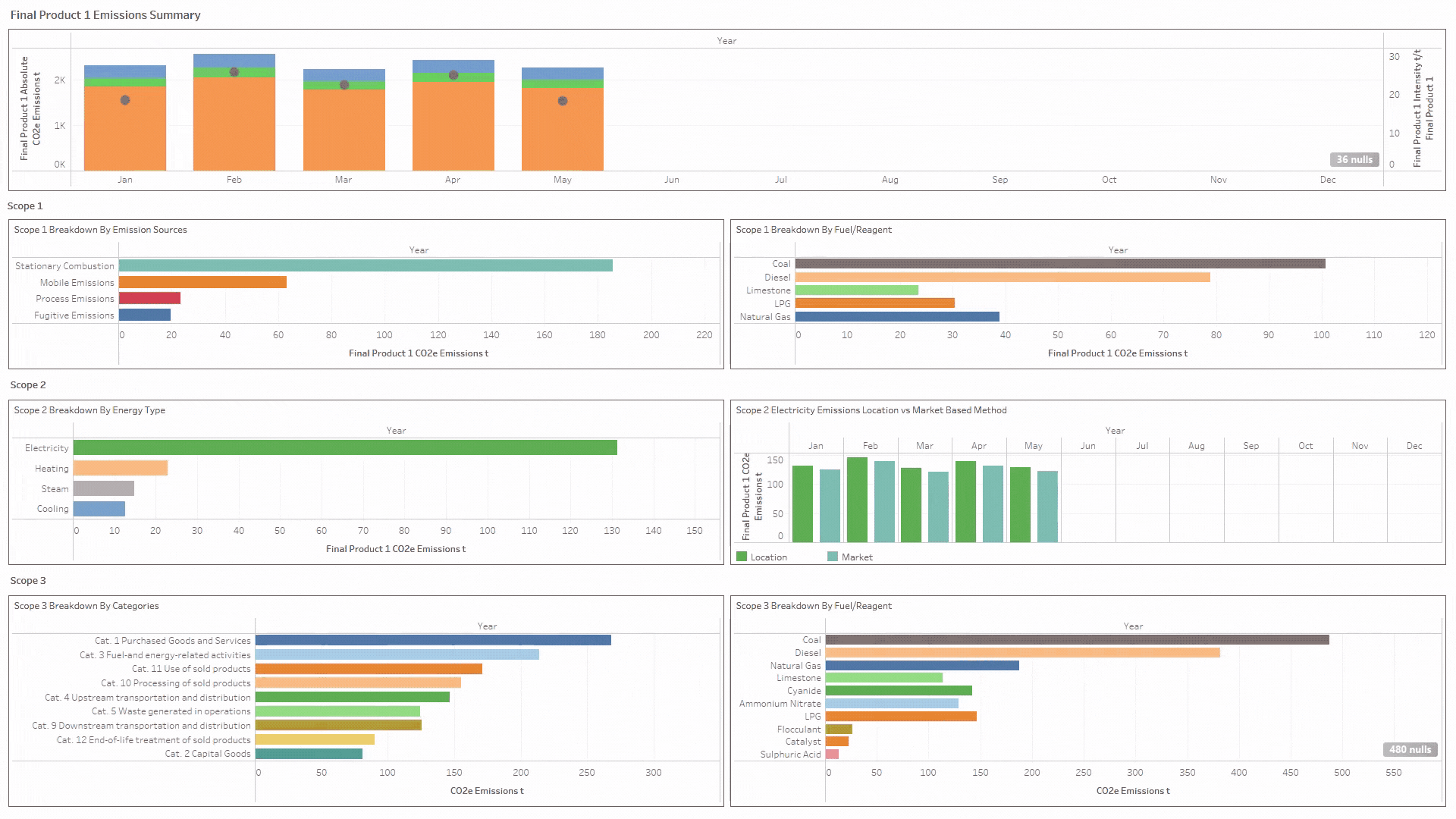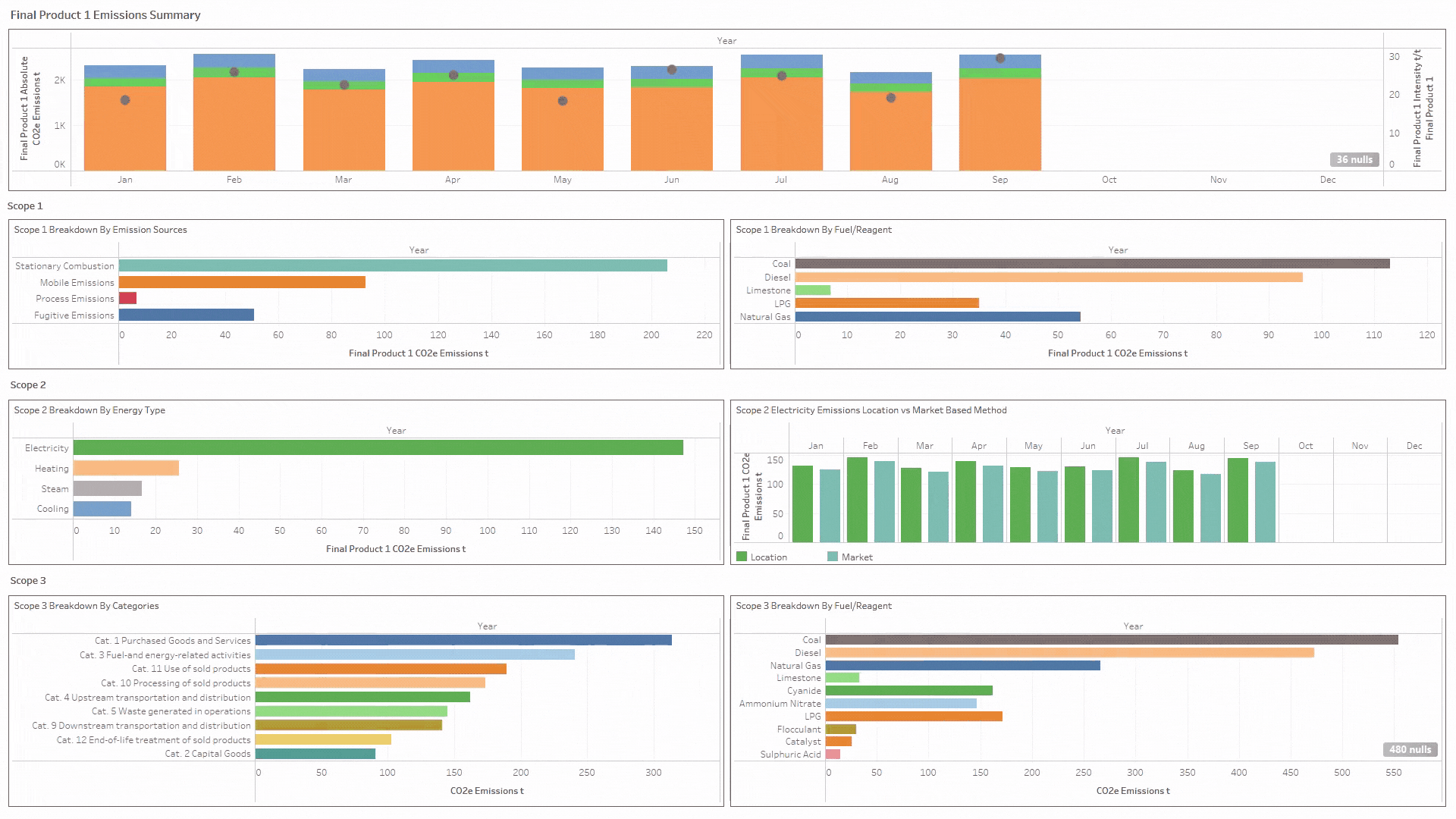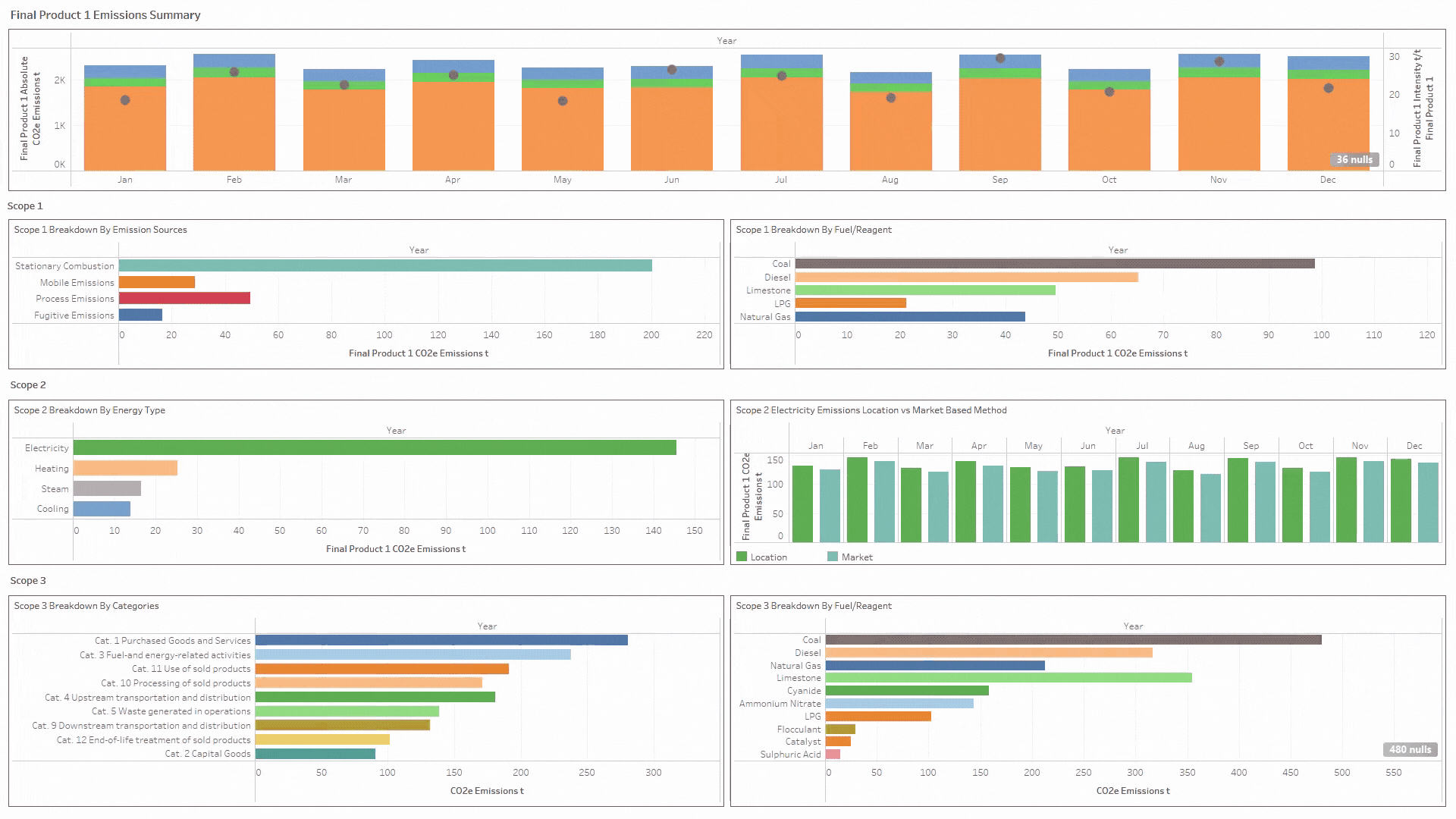
Designed to navigate multiple global frameworks and many separate ESG performance indicators, MI Sustainability is a uniquely flexible and comprehensive sustainability reporting solution for today, and the future.
- Track end-to-end sustainability indicators spanning Scopes 1, 2 & 3, and Climate & Nature
- Single source of centralised, validated, organised and integrated sustainability data
- Accurate plant-wide mass and energy balance customised to your exact process as a digital replica of your operations
- Contextualise your measured activity data using source data as inputs
- Analyse, track and report activity data right down to a product level
- Track and consolidate on-site and off-site renewable energy sources
- Capture and report on data directly related to the mining asset it has been implemented in, including integration with third party data
- Track, simulate, test, analyse and forecast scenarios
- Future-proof technology delivered in a scalable cloud-based SaaS platform
Choose the MI Sustainability package to suit you
Wherever you are along your sustainability reporting journey, MI Sustainability provides a flexible roadmap from ticking today’s compliance boxes through to advanced environmental, social and governance (ESG) capabilities.
MI Sustainability Standard supports organisations with ESG reporting across major voluntary and mandatory global frameworks and disclosure regulations.
It delivers centralised records that capture in-depth ESG data and supports compliance with evolving corporate sustainability reporting requirements.
On top of centralised data, MI Sustainability Advanced adds automated data capture and data quality reporting.
It includes data cleansing, organisation and validation tools (to assess data health and integrity), and advanced visualisation tools to deliver dynamic, accurate and auditable sustainability reports.
Beyond data automation, MI Sustainability Expert offers finance-grade sustainability reporting and automated validation of ESG data against mining and mineral operations data using a mass and energy balance configured to your site/s.
It includes intelligent data accrual mechanisms to complete data gaps, built-in alerts and monitoring, custom process optimisation and product carbon footprinting (PCF).
Building on these capabilities, MI Sustainability Enterprise delivers the granular analysis needed to plan, execute and evaluate your decarbonisation roadmap.
Running a steady-state simulation of your asset, it uses validated finance-grade production data to enable complex forecasting, transition planning and scenario analysis. You can adjust inputs and compare final production, emissions and consumption with advanced visualisation tools.
Delivering real-world results
Digital tracking uncovers $US1.5M per year in unused power
From under reporting sulphuric acid emissions by 26% to paying millions for unused power over time, we look at three examples where our digital sustainability platform delivered tangible results.
Global compliance and less carbon tax for hydrometallurgical facility
Our solution helps this industrial leader in Africa meet tighter compliance regulations, track electricity use, minimise their carbon tax bill and deliver mandatory auditable reports.
Using data to reduce the carbon footprint of battery production
We empowered a battery producer to cut emissions and waste by measuring an accurate reporting baseline, setting targets and testing scenarios using steady-state simulation technology.
A full suite of software to optimise your plant
Take control of your GHG sustainability reporting. Get started today.
References
- World Economic Forum (WEF), Digital solutions can reduce global emissions by up to 20%, 2022








